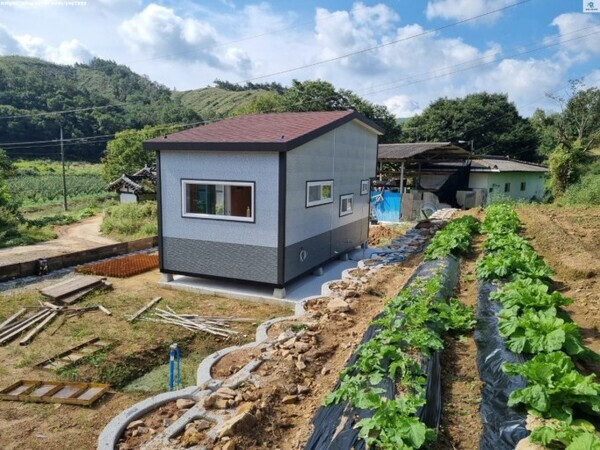
This opens the way for ‘rural stay-type shelters’ to be installed on farmland for more than 12 years. Installation of agricultural equipment sales facilities is permitted within agricultural promotion zones.
The Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs announced that it will announce legislation by December 9th for the ‘Agricultural Land Act Enforcement Decree and Enforcement Rules Amendment Bill’ containing these contents.
This revision reflects most of the government's plan to introduce rural stay-type shelters announced in August. First, the enforcement ordinance specified the basis for installing a temporary building-type rural stay-type shelter without converting farmland. The total floor area must be less than 33㎡ (10 pyeong) excluding auxiliary facilities such as deck, septic tank, and parking lot. However, the farmland area must be at least twice the combined area of the rural stay-type shelter and auxiliary facilities, and farming obligations are imposed.
It was decided to introduce a plan to extend the retention period (period of use), which was the biggest issue, from 12 years. Even after extending the retention period for the first 3 years and up to 3 times for 3 years each, if necessary, the policy is to allow it to be extended by 3 years each through the local government's building ordinance as long as it does not harm safety, function, aesthetics, or the environment.
Yoon Won-seup, director of agricultural policy at the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs, said, “We plan to prepare specific standards (regarding additional extension) through consultation with local governments.” “I think we will be able to manage the administrative management much more closely than at the farmhouse,” he said.
The scope of roads where rural stay-type shelters can be installed has also been clearly determined. In accordance with the ‘Rural Road Maintenance Act’, it was defined as a de facto road on which roads such as shaved roads, remote roads, rural roads, fire trucks, and emergency vehicles could pass, allowing the construction of rural lodging-type rest areas not only on statutory roads but also on farmland adjacent to existing roads. In addition, in order to resolve the inconvenience of existing farm hut users, improvements were made to exclude the area of auxiliary facilities such as decks and septic tanks from the total floor area of 20 m2 (6 pyeong) of the farm hut.
The ‘Farm Land Act Enforcement Decree Amendment Bill’ also established new regulations allowing regional and product agricultural cooperatives to install agricultural equipment sales facilities within agricultural promotion zones. However, it must be installed on the site of agricultural, livestock and forestry product processing and processing facilities and agricultural production distribution facilities, and the area is limited to less than 20% of the total facility area.
In addition, in rural specialized districts such as rural industrial districts and rural convergence industrial districts, and smart agriculture promotion districts, a basis has been created for the installation of all types of vertical farms without separate farmland conversion procedures. As a sub-statutory mandate of the ‘Farmland Act’ revised in January this year, regulations such as ▲ procedures for establishing basic and implementation plans for farmland management ▲ standards for fines for non-compliance with the obligation to report changes in land use ▲ procedures for reporting farmland improvement (filling and cutting) were also established.
[Copyright (c) Global Economic Times. All Rights Reserved.]